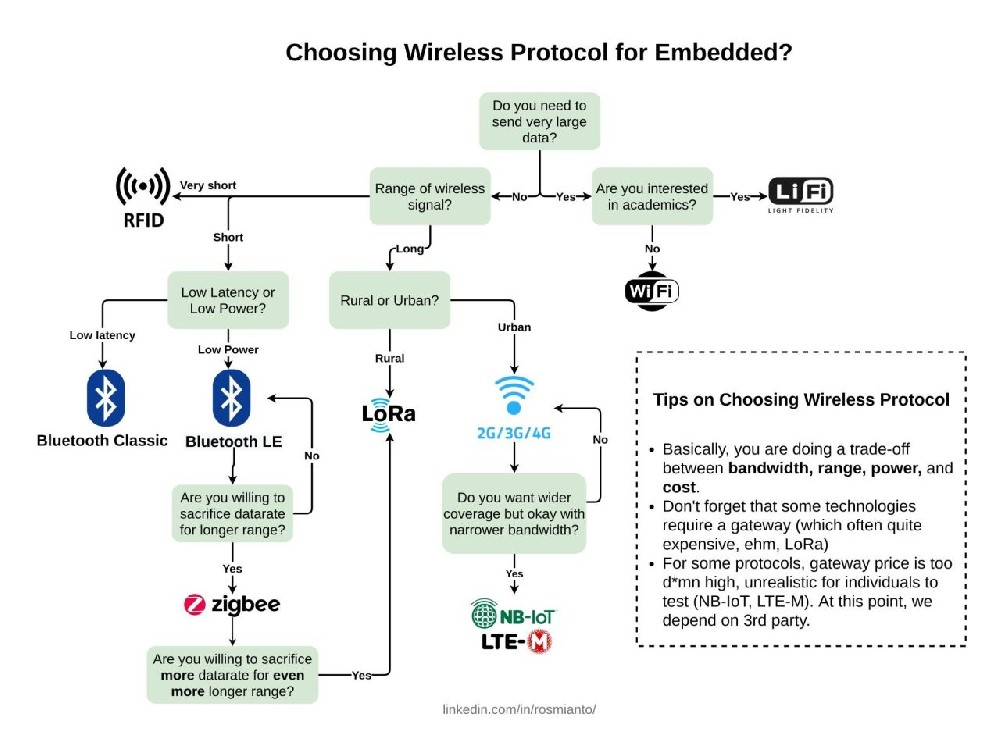
"2G, 4G, IOT, CAT1, CATM, and LoRa"The regions where 2G, 4G, IOT, CAT1, CATM, and LoRa are mainly used now are as follows:• 2G: 2G is a second-generation cellular technology that supports voice and l...
"2G, 4G, IOT, CAT1, CATM, and LoRa"
The regions where 2G, 4G, IOT, CAT1, CATM, and LoRa are mainly used now are as follows:
• 2G: 2G is a second-generation cellular technology that supports voice and low-speed data services. 2G networks are still widely used in some parts of the world, such as Africa, Asia, and Latin America, where they provide basic connectivity and coverage for low-income populations.
However, 2G networks are gradually being phased out by carriers in favor of more advanced technologies like 3G, 4G, and 5G.
• 4G: 4G is a fourth-generation cellular technology that supports high-speed data services and multimedia applications. 4G networks are based on LTE (Long Term Evolution) standards, which offer faster speeds, lower latency, and better quality than 3G networks.
4G networks are widely deployed and serve as the de facto standard for cellular communications in most parts of the world, such as North America, Europe, Australia, and Japan. However, 4G networks are also evolving to support new IoT-specific standards like LTE-M and NB-IoT.
• IOT: IOT stands for Internet of Things, which refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, sensors, and other objects that can communicate and exchange data over the internet.
IOT devices can use various communication technologies to connect to the internet, such as WiFi, Bluetooth, Ethernet, or cellular. Among the cellular technologies, there are different standards that are designed for IoT applications, such as LTE-M, NB-IoT, and Cat-1.
• CAT1: Cat-1 is an LTE standard that supports data rates of up to 10 Mbps for downlink and 5 Mbps for uplink.
Cat-1 is suitable for IoT devices that require moderate bandwidth and low latency, such as video surveillance cameras, smart meters, vending machines, and vehicle telematics. Cat-1 is widely available and has global coverage across many carriers
• CATM: Cat-M is also known as LTE-M or Cat-M1. It is an LTE standard that supports data rates of up to 1 Mbps for both downlink and uplink. Cat-M is designed for IoT devices that require low power consumption, extended battery life,
improved indoor coverage, and enhanced securityh. Cat-M is ideal for applications such as asset tracking, smart wearables, health monitoring, and smart city solutionsh. Cat-M is relatively new and has limited coverage in some regions.
• LoRa: LoRa is a low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) technology that operates on the unlicensed spectrum. LoRa supports data rates of up to 50 kbps and has a long range of up to 15 km in rural areas and 5 km in urban areas.
LoRa is designed for IoT devices that require low bandwidth and long battery life, such as environmental sensors, smart agriculture, and wildlife tracking LoRa is not a cellular technology but a radio frequency technology that requires dedicated gateways
and servers to connect to the internet. LoRa is widely adopted by many IoT service providers and has a large ecosystem of devices and applications.